Liver Function Tests (LFT)
When and Why They’re Done
When and Why They’re Done
You are here >> Home > Blog > Cancer > Cancer Diagnosis > Diagnosis English > Liver Function Tests
Understanding your health reports can sometimes feel confusing, but it doesn’t have to be. This guide will explain everything about Liver Function Tests in a very simple and easy-to-understand way. We will cover what these tests are, why they are done, what the results mean, and how you can keep your liver healthy. Whether your doctor has recommended an LFT or you are just curious about your health, this article will answer all your questions.
Summary
- Enzymes that rise with injury (ALT/AST)
- Bile flow markers (ALP & GGT)
- Liver’s making power (Bilirubin, Albumin, INR)
What Are Liver Function Tests?
By looking at these levels, doctors can get a clear picture of your liver’s health. It helps them diagnose liver diseases, monitor the progress of a treatment, or see how a particular medicine is affecting the liver. It’s a very common and important tool for maintaining your overall health.
- History
- Definition and purpose of LFT
The key goals of performing Liver Function Tests are:
⦿ Screening for Liver Infections: To check for infections like hepatitis.
⦿ Monitoring Disease Progression: To see if a known liver disease like cirrhosis is getting better or worse.
⦿ Evaluating Treatment: To understand if a treatment for liver disease is effective.
⦿ Checking for Medication Side Effects: Some medicines can affect the liver, and LFTs help monitor this.
⦿ Assessing Liver Damage: To determine the extent of damage or scarring (cirrhosis) in the liver.
- What do abnormal LFT results mean?
An abnormal result is simply a signal for your doctor to investigate further. It means that the levels of certain enzymes or proteins are outside the normal range. For example, high enzyme levels might suggest inflammation or damage to liver cells, while low protein levels could mean the liver’s production function is weak. Your doctor will interpret the results based on your overall health, symptoms, and medical history.
Types of Liver Function Tests
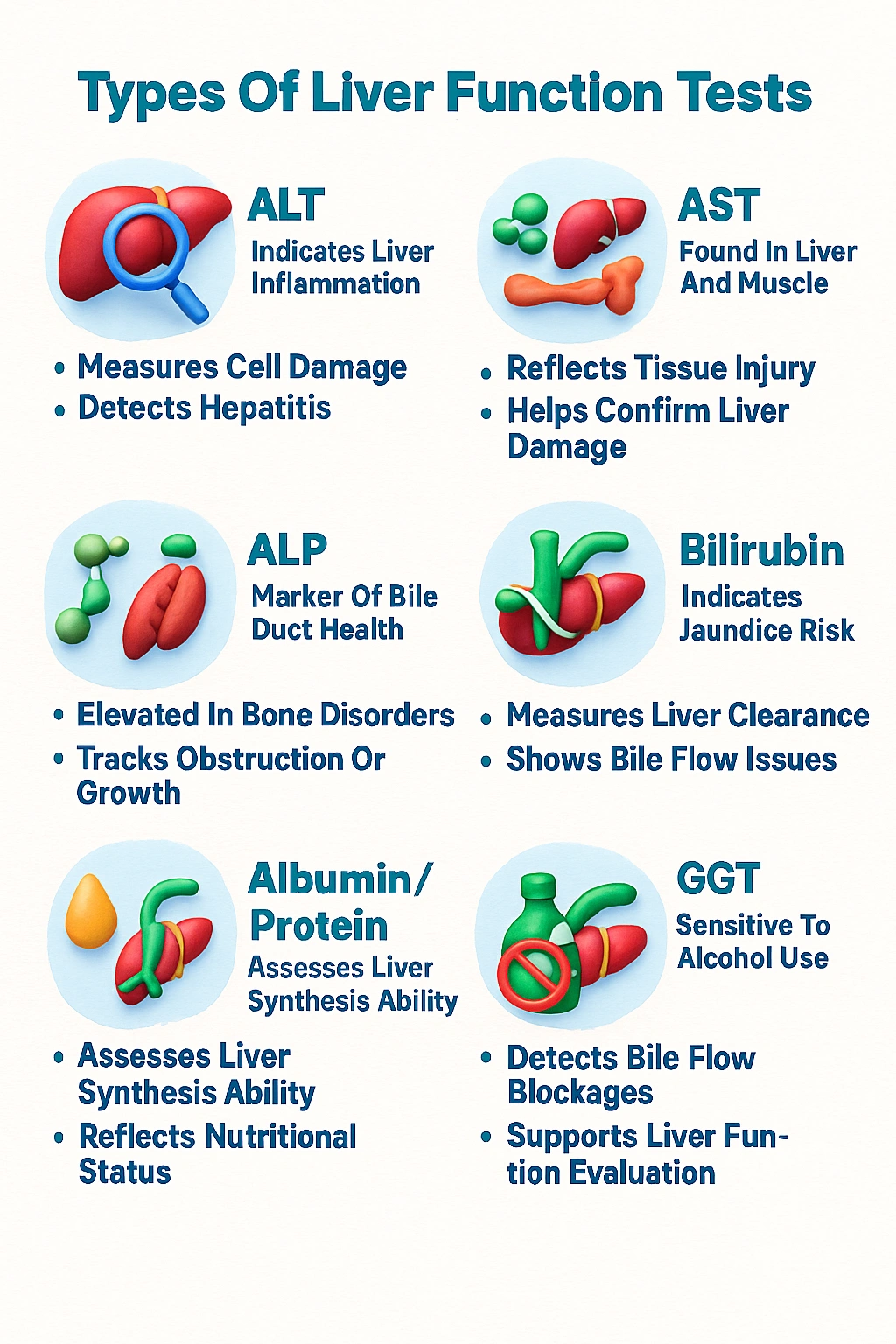
- Alanine transaminase (ALT) test
- Aspartate transaminase (AST) test
- Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) test
- Bilirubin levels (direct and total)
- Albumin and total protein tests
- Gamma-glutamyl transferase (GGT)
- Key Components of a Liver Function Test and Their Roles
| Test Name | What It Measures | What Abnormal Levels Might Mean |
|---|---|---|
| Alanine Transaminase (ALT) | An enzyme primarily found in the liver. | High levels strongly suggest liver cell damage or inflammation (e.g., from hepatitis). |
| Aspartate Transaminase (AST) | An enzyme found in the liver, heart, and muscles. | High levels can indicate liver damage, but also issues with other organs. |
| Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP) | An enzyme found in the liver, bile ducts, and bones. | High levels often point towards blocked bile ducts, gallstones, or certain liver diseases. |
| Bilirubin | A waste product from the breakdown of red blood cells. | High levels can cause jaundice and may indicate problems with the liver's ability to process waste. |
| Albumin | A key protein made by the liver. | Low levels can signal chronic liver disease or cirrhosis, as the liver's ability to produce protein is reduced. |
Why Are Liver Function Tests Done?
- To detect liver diseases early
- To monitor ongoing liver conditions
- To check liver health before medications
- During routine health checkups
Symptoms That May Require an LFT Test
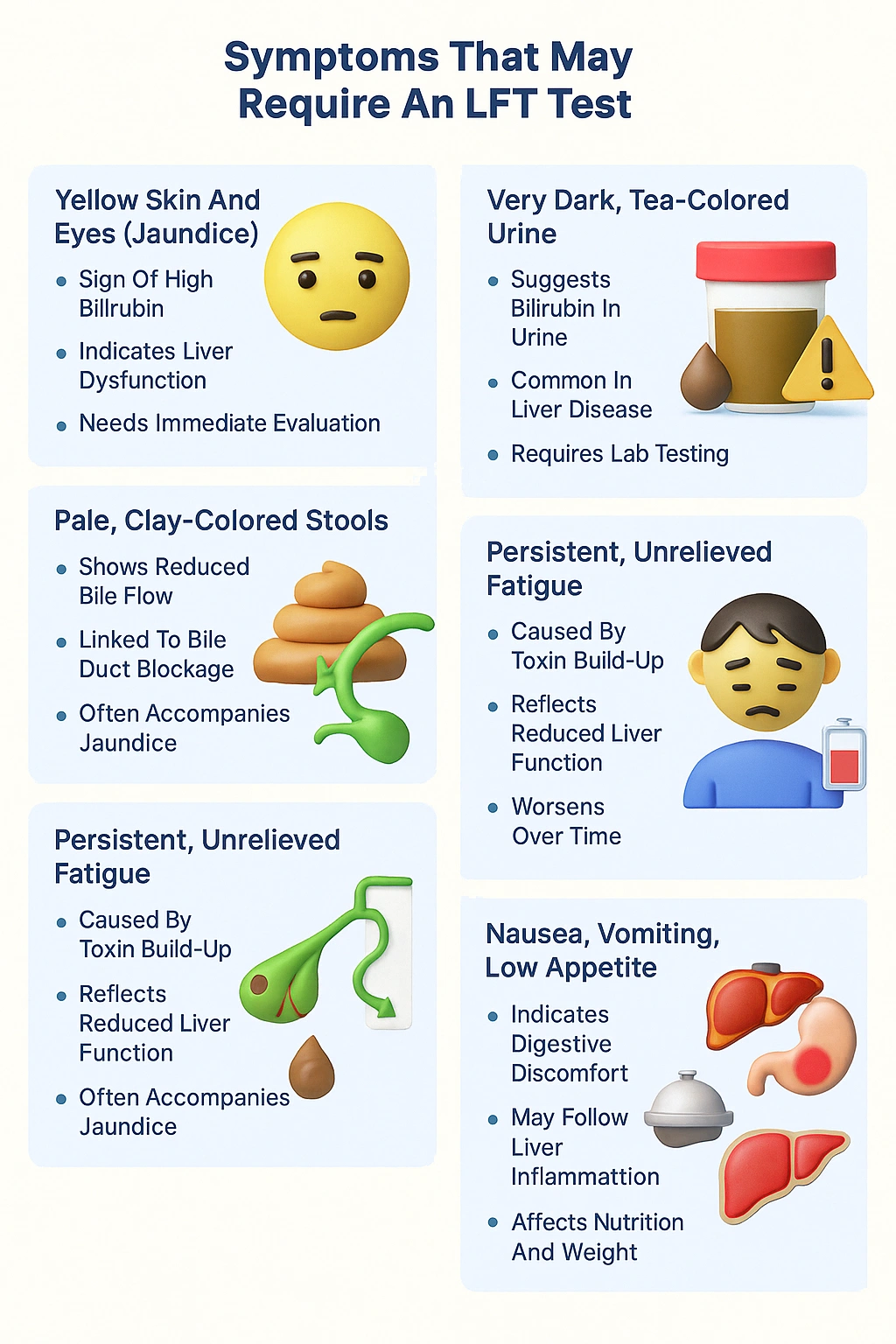
- Yellowing of skin and eyes (jaundice)
- Fatigue, nausea, or abdominal pain
- Unexplained weight loss or swelling

How to Prepare for Liver Function Tests

- Fasting and food restrictions
- Medication and alcohol intake advice
- Discussing health history with doctor
Normal Ranges of Liver Function Tests
- Reference values for key liver enzymes
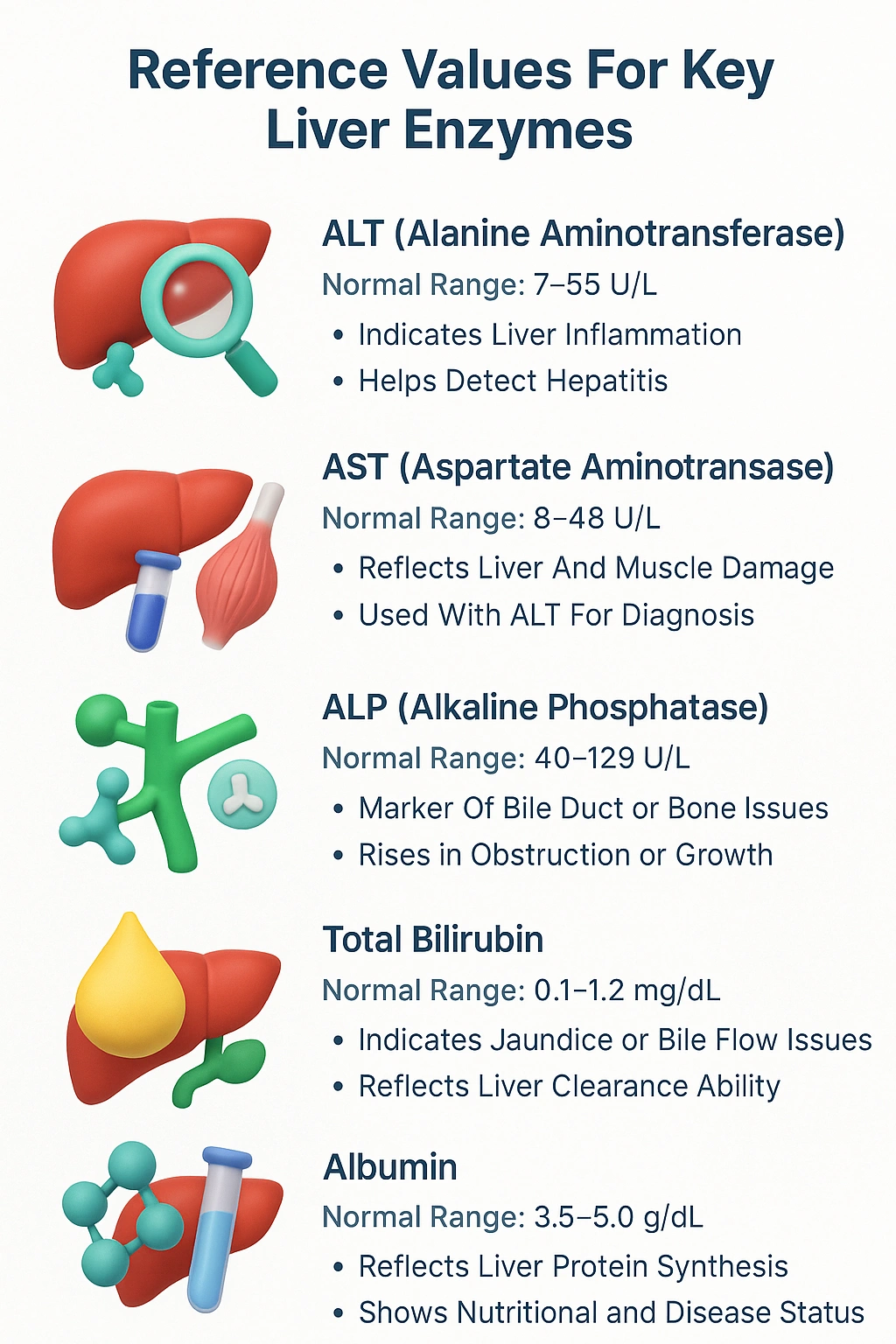
⦿ ALT (Alanine Transaminase): 7 to 55 units per liter (U/L)
⦿ AST (Aspartate Transaminase): 8 to 48 U/L
⦿ ALP (Alkaline Phosphatase): 40 to 129 U/L
⦿ Total Bilirubin: 0.1 to 1.2 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL)
⦿ Albumin: 3.5 to 5.0 grams per deciliter (g/dL)
- Interpreting results with your doctor
Your doctor will also consider your symptoms, medical history, and a physical examination to form a complete picture. You might find a liver function tests interpretation pdf online, but it cannot replace a professional medical opinion.
- When are values considered alarming?
- Understanding Normal vs. Abnormal LFT Ranges
| Test Parameter | Typical Normal Range | Potential Meaning of High Levels | Potential Meaning of Low Levels |
|---|---|---|---|
| ALT | 7 - 55 U/L | Liver cell damage (hepatitis, fatty liver, drug injury). | Generally not a concern. |
| AST | 8 - 48 U/L | Liver damage, muscle injury, or heart problems. | Generally not a concern. |
| ALP | 40 - 129 U/L | Blocked bile ducts, gallstones, bone disorders. | Malnutrition, zinc deficiency (rare). |
| Total Bilirubin | 0.1 - 1.2 mg/dL | Liver disease, bile duct blockage, Gilbert's syndrome. | Generally not a concern. |
| Albumin | 3.5 - 5.0 g/dL | Inflammation, shock, malnutrition. (A liver function test total protein high result might indicate other issues). | Chronic liver disease (cirrhosis), kidney disease, malnutrition. |
Causes of Abnormal Liver Function Test Results
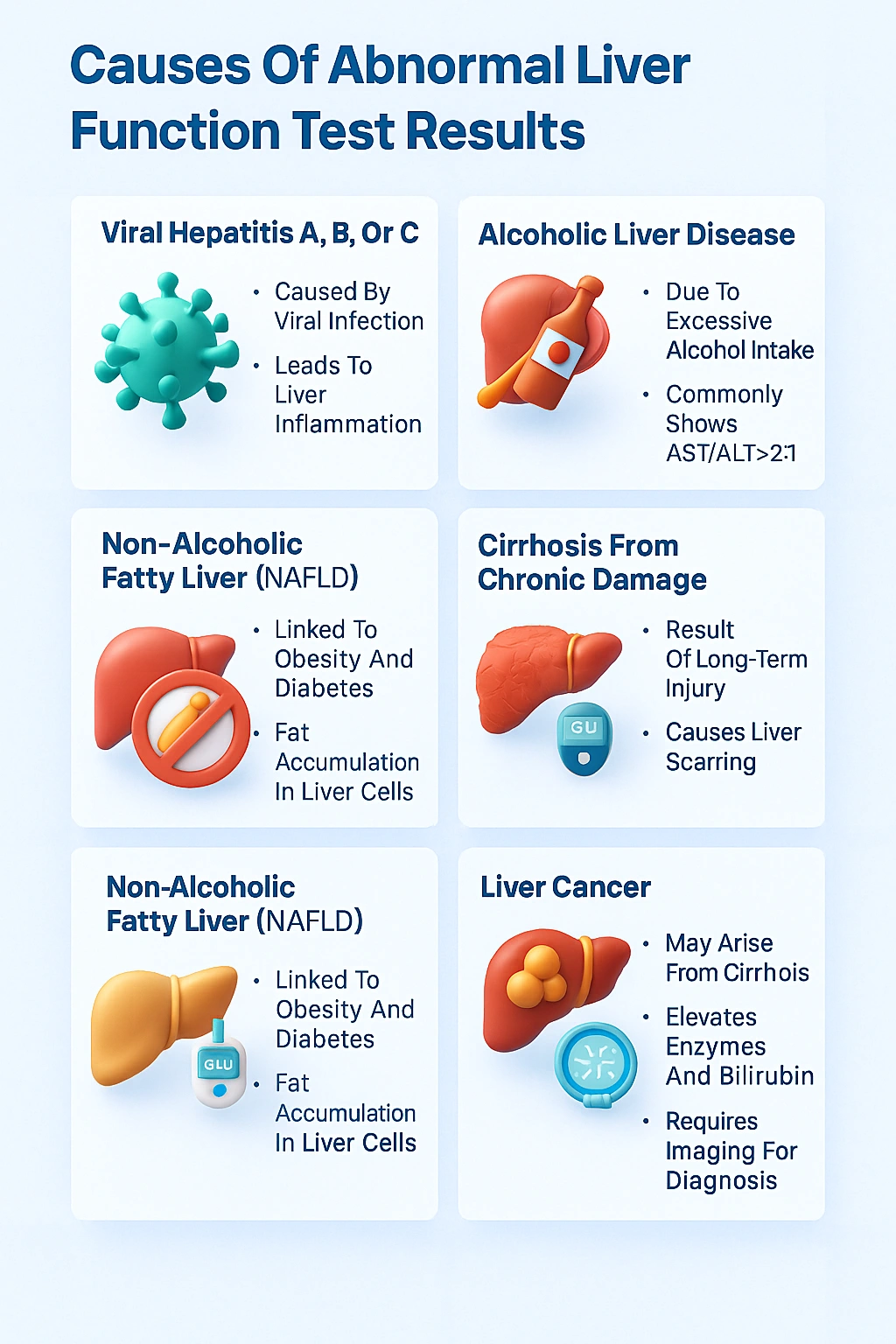
- Viral hepatitis (Hepatitis A, B, C)
- Alcoholic liver disease and fatty liver
- Cirrhosis and liver cancer
- Drug-induced liver injury
Follow-Up After Abnormal LFTs
- Imaging tests (ultrasound, CT, MRI)
After an abnormal LFT, one of the most common follow-up steps is an imaging test. These tests create pictures of your liver and surrounding organs.
⦿ Ultrasound: This uses sound waves to create images and is very good for detecting issues like fatty liver, cysts, tumors, or problems with the gallbladder, such as liver function tests gallstones.
⦿ CT Scan (Computed Tomography): This provides more detailed, cross-sectional images of the liver and can help identify tumors or other structural abnormalities.
⦿ MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): This uses magnets and radio waves to produce very detailed images and is excellent for examining soft tissues and bile ducts.
- Liver biopsy or fibroscan
In some cases, the doctor might need to examine a small piece of your liver tissue directly. This is done through a liver biopsy. A thin needle is used to take a tiny sample of the liver, which is then examined under a microscope. This can help determine the exact type and extent of liver damage.
A less invasive alternative is a FibroScan. This is a special type of ultrasound that measures the stiffness of the liver. A stiffer liver usually means more scarring (fibrosis or cirrhosis), and this test can help assess the level of damage without a biopsy.
- Lifestyle changes and medications
Once the cause of the abnormal LFT is identified, treatment can begin. This often involves a combination of lifestyle changes and medications.
⦿ Lifestyle Changes: Your doctor will likely advise you to stop drinking alcohol, lose weight if you are overweight, eat a healthy diet, and get regular exercise. These changes can significantly improve liver health, especially in cases of fatty liver disease.
⦿ Medications: Depending on the diagnosis, you may be prescribed medications. For example, antiviral drugs are used to treat chronic hepatitis B or C. Other medicines might be used to manage symptoms or complications of liver disease.
Preventing Liver Problems
- Healthy diet for liver health
What you eat has a direct impact on your liver. A healthy, balanced diet can help prevent conditions like fatty liver disease.
⦿ Eat Plenty of Fruits and Vegetables: They are rich in antioxidants, which protect liver cells from damage.
⦿ Choose Whole Grains: Foods like oats, brown rice, and whole-wheat bread are high in fiber, which helps the liver.
⦿ Include Lean Protein: Opt for fish, chicken, beans, and lentils.
⦿ Drink Coffee: Some studies suggest that moderate coffee consumption can be good for the liver.
⦿ Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day.
- Avoiding alcohol and processed foods
Some things are particularly hard on your liver and should be limited or avoided.
⦿ Alcohol: Alcohol is a toxin that your liver has to process. Excessive drinking is a leading cause of liver damage.
⦿ Processed Foods: Foods high in sugar, salt, and unhealthy fats (like fast food, packaged snacks, and sugary drinks) can contribute to fat buildup in the liver and cause inflammation
⦿ Saturated and Trans Fats: Limit your intake of red meat and fried foods.
- Regular health checkups and LFTs
- Vaccination and hygiene practices
You can protect your liver from viral hepatitis by getting vaccinated. Vaccines are available for Hepatitis A and Hepatitis B. Practicing good hygiene, such as washing your hands thoroughly, is also important to prevent the spread of Hepatitis A. To avoid Hepatitis B and C, never share needles, razors, or toothbrushes, and ensure any tattoos or piercings are done with sterile equipment.
- Liver-Friendly Foods and Foods to Limit
| Foods to Include for a Healthy Liver | Foods to Limit or Avoid | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| Oatmeal, Brown Rice, Whole Grains | Sugary Sodas, Packaged Snacks, Sweets | Fiber helps with digestion and reduces stress on the liver. High sugar can lead to fat buildup in the liver. |
| Broccoli, Spinach, Leafy Greens | Fried Foods, Fast Food | These vegetables are packed with antioxidants that protect the liver from damage. Unhealthy fats cause liver inflammation. |
| Garlic, Onions, Turmeric | Excess Salt, Canned Soups, Processed Meats | These contain compounds that help the liver detoxify the body. High salt intake can lead to fluid retention and strain the liver. |
| Green Tea, Coffee (in moderation) | Alcohol, Beer, Wine | Antioxidants in these beverages may help reduce the risk of liver disease. Alcohol is a direct toxin to liver cells. |
| Lean Protein (Fish, Chicken, Beans) | Red Meat, Full-Fat Dairy | Provides essential amino acids without adding excessive saturated fat. Saturated fats contribute to fatty liver disease. |
Frequently Asked Questions

Dr. Harsh Shah
MS, MCh (GI cancer Surgeon)
Dr Harsh Shah is a well known GI & HPB Robotic Cancer Surgeon in ahmedabad. He treats cancers of esophagus, stomach, liver, pancreas, colon, rectum & small intestines. He is available at Apollo Hospital.

